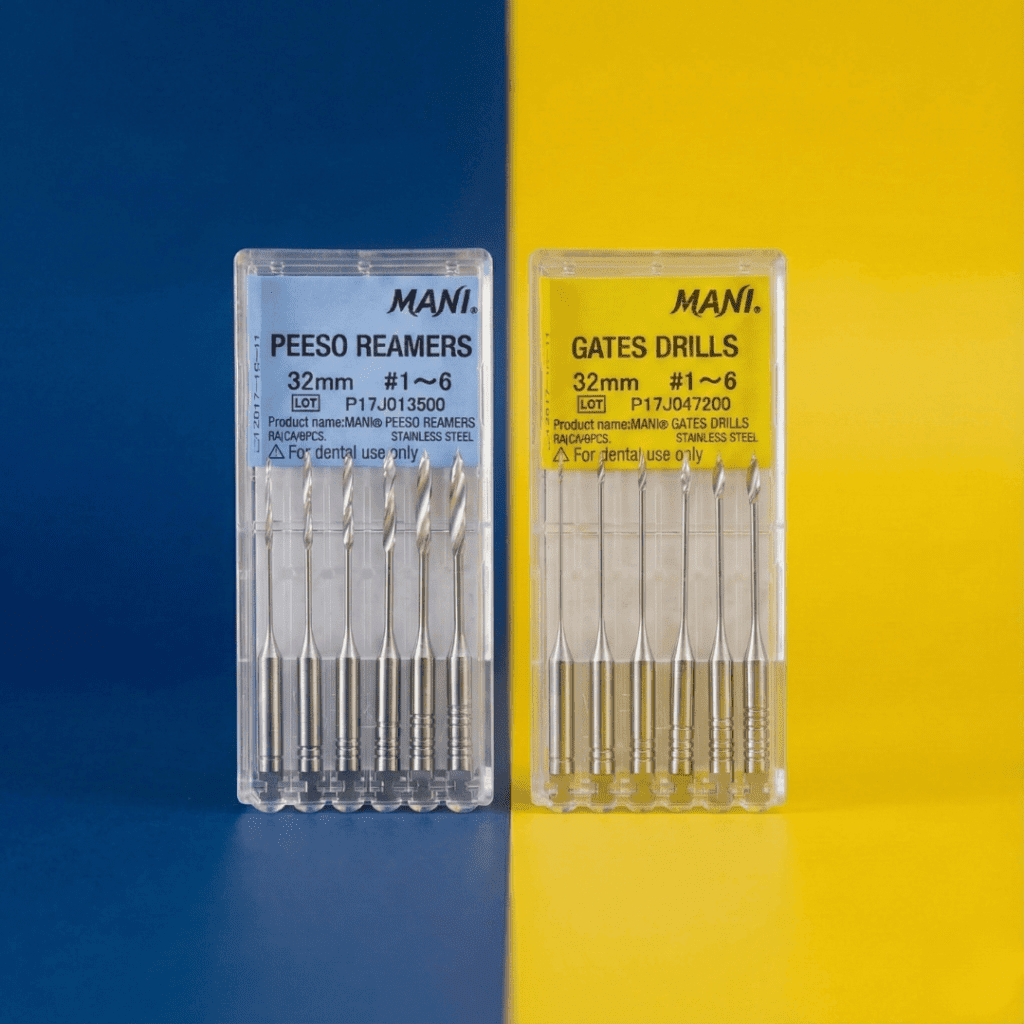
Effective endodontic therapy depends on predictable canal shaping, adequate coronal flaring, and unobstructed irrigation pathways. MANI Peeso Reamers and Gates Drills are engineered to support these objectives through precise cutting performance, controlled enlargement, and high structural integrity under repeated clinical use.

Optimized for Coronal Enlargement and Post-Space Preparation
Peeso Reamers and Gates-Glidden Drills are widely utilized for:
Coronal and middle-third canal enlargement
Initial shaping to improve straight-line access
Facilitating irrigant penetration and debris elimination
Post-space preparation (particularly with Peeso Reamers due to their parallel cutting design)
The instruments are designed with non-cutting pilot tips, which help maintain centered advancement along the canal path and reduce the likelihood of procedural complications such as lateral perforation or ledge formation.
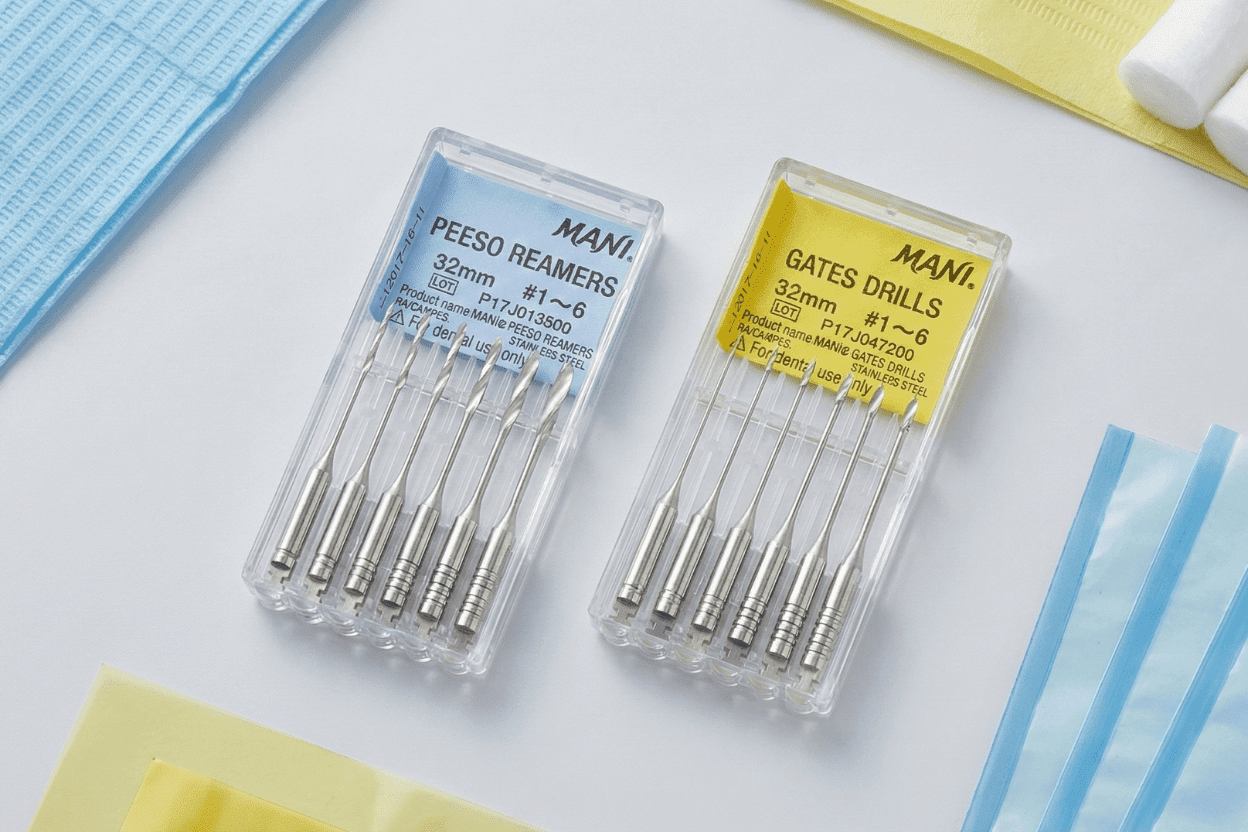
Fast and Intuitive Size Identification
Efficiency is elevated through clear groove markings on the instrument shank, making size identification immediate and error-free. In a clinical environment where every second matters, intuitive instrument recognition supports smoother workflow and reduces chances of selecting the wrong size.
Because in endodontics, precision should never come with guesswork.
Reliability You Can Trust
The MANI brand stands by its philosophy:
“The best quality in the world, to the world.”
This commitment is reflected in the manufacturing standards, material selection, and performance consistency of Peeso Reamers and Gates Drills—making them a trusted choice for dental professionals worldwide.
Explore the Products
🔗 MANI Peeso Reamers:
https://mani-malaysia.com/product/mani-peeso-reamers/
🔗 MANI Gates Drills:
https://mani-malaysia.com/product/mani-gates-drills/
Regulatory Information
Registered under Act 737.
MDA Registration Numbers:
• GB6711523-130147 – Peeso Reamers
• GB6508723-143971 – Gates Drills
THIS POST IS INTENDED FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS ONLY.
APA-Style References
American Association of Endodontists. (2020). Guide to clinical endodontics (7th ed.). AAE.
Ingle, J. I., Fouad, A. F., & Siqueira, J. F. (Eds.). (2019). Ingle’s endodontics (7th ed.). BC Decker.
Peters, O. A. (2004). Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: A review. Journal of Endodontics, 30(8), 559–567. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.DON.0000129039.59003.9D
Srikumar, G. P., & Hebbar, A. (2017). Comparison of instrument design and material properties in endodontic rotary and stainless-steel instrumentation. International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Health, 3(6), 1–6.
Torabinejad, M., & Walton, R. E. (2014). Endodontics: Principles and practice (5th ed.). Saunders.



